Component, Morphology and Function of Blood
- bloggy hls
- May 5, 2021
- 3 min read
Updated: May 7, 2021
What is the blood doing in human body ?
Blood is one of connective tissue in human. Blood have 3 major functions:
The first one is transportation. Blood help transport oxygen to other cells from various body parts and the blood also remove carbon dioxide from tissues to lung to be exhaled.
The second function is regulation. Blood helps in heat regulation and balancing pH and water throughout the body.
Last function is blood acts as protection. Blood consist of white blood cells to get rid off pathogen and contained platelets for blood clotting.
What is the is it in human blood?
Blood consist of 55% plasma and 45% blood cell. The plasma is a portion of blood. Plasma contain 92% water, &% protein which is albumin, globulin and fibrinogen. And also 1% of nutrients.
There are three types of blood cell which is Erythrocytes, Leukocyte and Thrombocyte.
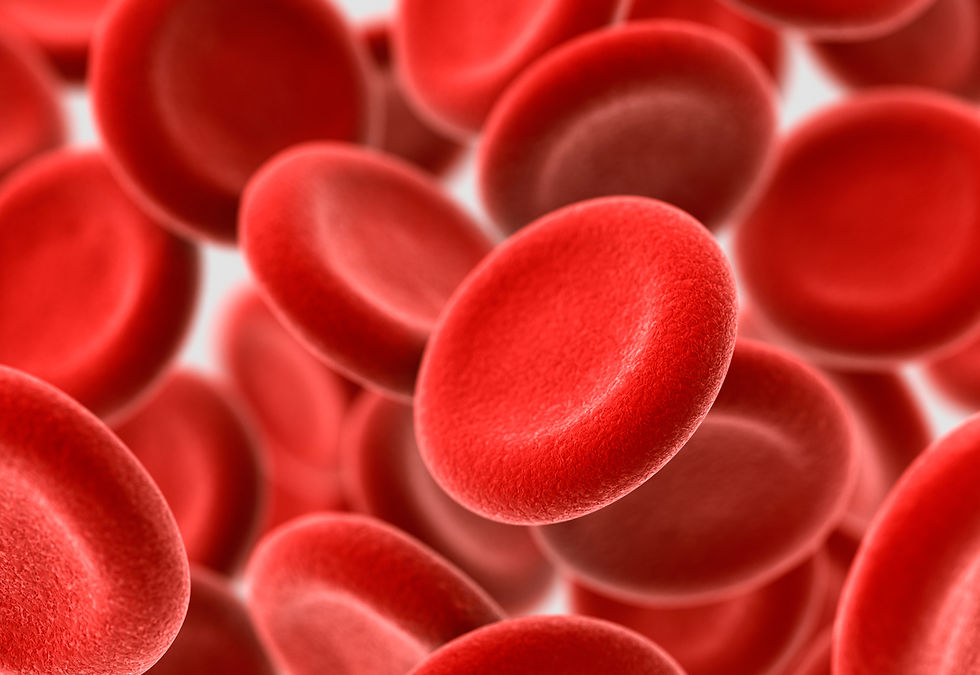
The erythrocyte or the red blood cell help in carrying oxygen and transport carbon dioxide through our body. RBC is biconcave disc shape to allow diffusion of the oxygen and carbon dioxide. It consist of pigment called hemoglobin that helps to bind of carbon dioxide and oxygen. RBC was produced in bone marrow and have 120 days life span.
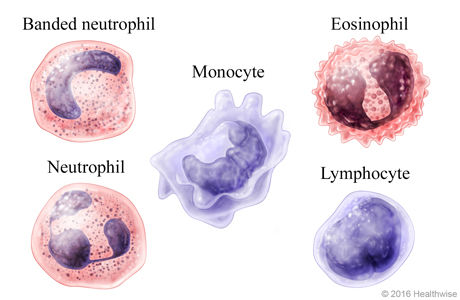
The leukocyte or the white blood cell function to fight off the pathogen. There are many types of leukocyte:
Neutrophils is the most abundant type of leukocyte. It consist of nucleus 2-5 lobes that connected by fine filament and transparent cytoplasm with pink coloured granule. Neutrophils function against bacterial infection and inflammation. Neutrophils is the first responders to bacterial infection.
Eosinophil deals with parasitic infection. It consist of bilobed nucleus, cytoplasm full with pink granules and cytoplasm rich in dark purple coloured granules. Only a few can be seen in normal blood.
Basophil deals with allergic reaction related with histamine. It was the rarest leukocyte because there only a few can be seen in normal blood. It consist of cytoplasm rich in dark purple coloured granules. It consist of bi/trilobed nucleus and it was hard to see the nucleus overlapped with granules.
Monocyte is the biggest leukocytes and kidney shaped nucleus. It has transparent cytoplasm with ground glass appearance. Monocyte has phagocytosis function. It can also bind to the pathogens and presenting them to T cells.
Lymphocyte commonly appeared (20-40%). Lymphocyte is smaller than other leukocytes, larger than rbc. It consist of transparent cytoplasm, round and large nucleus occupying most of cyctoplasm. There are 3 types lymphocyte which is T cell that coordinate immune system, defense against intracellular bacteria and kill virus infected cells.
The last blood cells in human body is thrombocyte or known as platelets is a small cells derived from precursor megakaryocyte. It does not have nucleus and mostly the thrombocyte is oval in shape. It has a life span 8-12 days and also a natural source of growth factor.
How the thrombocyte work?
The thrombocyte secrete a hormone called serotonin which constricts torn blood vessel. Then, the thrombocyte will accumulating at sites of injury sticking together to plug gaps in broken blood vessels. The thrombocyte rich in certain activator that activates some proteins found in plasma. These protein are thrown out in the form of fibers as network. This network traps the escaping RBC's and form a clot that will seal the blood vessel so bleeding is stopped.
References
Bassu, D. (2014). Overview of blood components and their preparation. Indian Journal Anaesthesia.
Sarode, R. (2021). Components of Blood. MSD Manual Consumer Version.




Comments